Self Monitoring
Blood Pressure Monitors for the Home
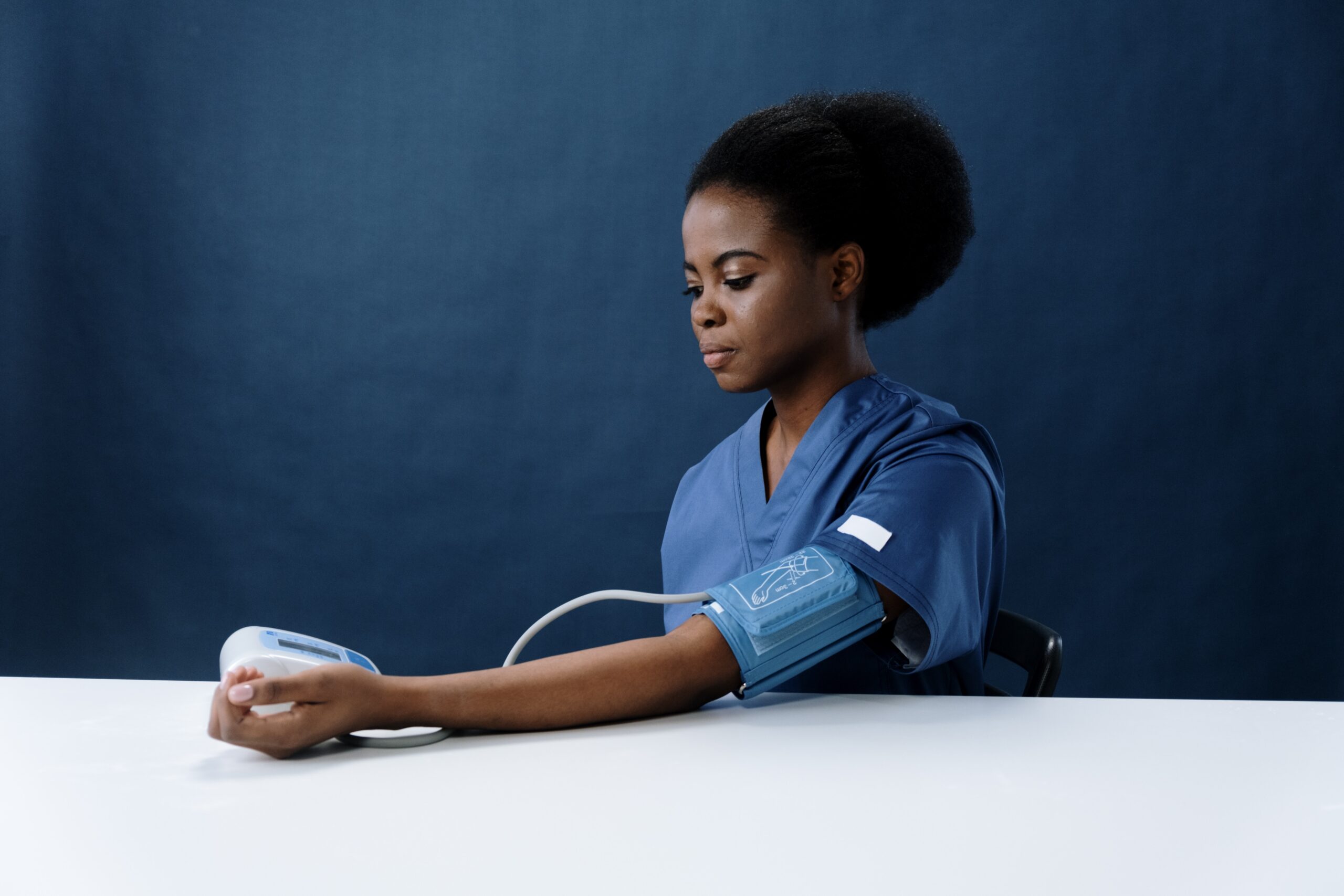
Everyday self-monitoring of blood pressure is a crucial step that people can take to maintain cardiovascular health and avoid the devastating repercussions that come with undiagnosed and untreated hypertension, according to medical professionals. Using an aneroid sphygmomanometer cuff and stethoscope is the conventional method of taking blood pressure readings. Although these devices are often precise and display the pressure on a dial, they do require some skill and training.
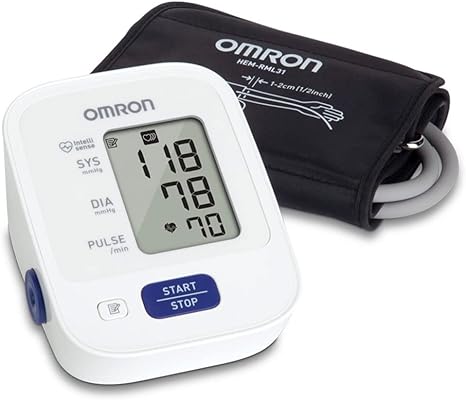
Individuals can now self-manage their blood pressure with a broad range of blood pressure monitors. The computerized device that shows the diastolic and systolic pressure on a screen is the most widely used. Patients with hearing impairments can benefit from the digital blood pressure monitoring technology because there’s no need to use a stethoscope to listen to heart sounds. A lot of these devices have charts that can be used to accurately record blood pressure readings, which can then be shared with a doctor.
Tips for Blood Pressure Monitoring:
- Relax for about 5 to 10 minutes before measurement.
- Remove constricting clothing and place cuff on bare arm.
- Sit comfortably with your left arm resting on a flat surface so that the center of your upper arm is at the same height as your heart.
- Unless your physician recommends otherwise, use left arm to measure pressure.
- Lay left arm on the table with palm up. Place the cuff on upper arm with the tube facing downward and toward the inside of your arm.
- The cuff should be snug but not too tight. You should be able to insert two fingers between the cuff and your arm.
- Remain still and do not talk.
- Take two readings one minute apart and record the results
 |
|
Translating Blood Pressure Numbers Monitoring Blood Pressure at home Understanding Hypertension Blood Pressure Awareness Blood Pressure Facts |