Blood Pressure Facts
What is blood pressure?
The force exerted by blood against the arterial walls. It is measured in millimeters of Mercury (mmHg). For example: 127/65 mmHg
Why measure blood pressure?
Blood pressure may be excessively: High = Hypertension or Low = Hypotension.
Either condition may lead to heart disease, organ damage, stroke, or early mortality
What are the guidelines for blood pressure measurements?
The following guidelines may be used for the assessment of blood pressure.
| Normal | Prehypertension | Stage 1 Hypertension |
Stage 2 Hypertension |
| < 120 and < 80 | 120-139 or 80-89 | 140-159 or 90-99 | >160 or >100 |
Please consult with your physician when interpreting blood pressure measurements.Factors affecting blood pressure:
- Age
- Weight
- Heredity
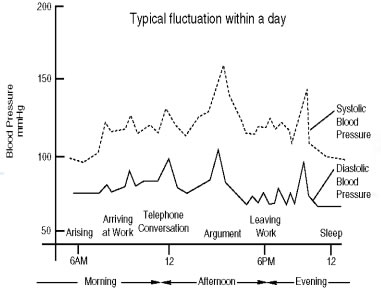
- Time of Day
- Physical Activity
- Emotional Stress
- Certain Foods
- Medications
Tips for Successful Blood Pressure Monitoring
Step 1) Select Correct Cuff Size. Measure upper arm circumference to determine your correct size
Step 2) Select the right monitor for you. Auto-inflation models are recommended for those who experience difficulty when squeezing inflation bulb.
Step 3) Read the instruction guide carefully. or speak with your physician.|
Self Monitoring your Blood Pressure Translating Blood Pressure Numbers Monitoring Blood Pressure at home Understanding Hypertension Blood Pressure Awareness |