Choosing a Blood Pressure Monitor
Blood Pressure Monitors
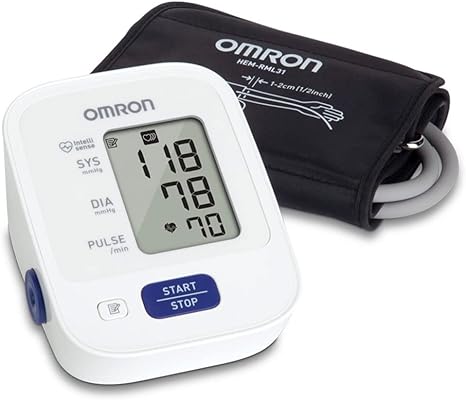
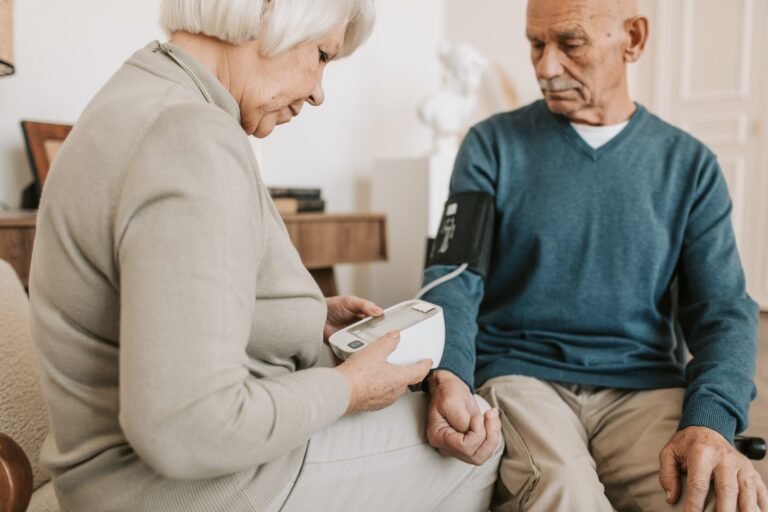
Automatic blood pressure monitors
Complete measurement readouts that are digitally displayed, precise, and easy to use. The “oscillometric method”—a non-invasive blood pressure measurement method—is the foundation of the technology. The measurement of the vibrations brought on by the arterial pulse is referred to as “oscillation”. Initially, the cuff is inflated until the artery is completely closed. After that, as the cuff deflates, the monitor measures. The pulsatile pressure that the artery wall produces as it expands and contracts against the cuff with each heartbeat is examined by blood pressure monitors.
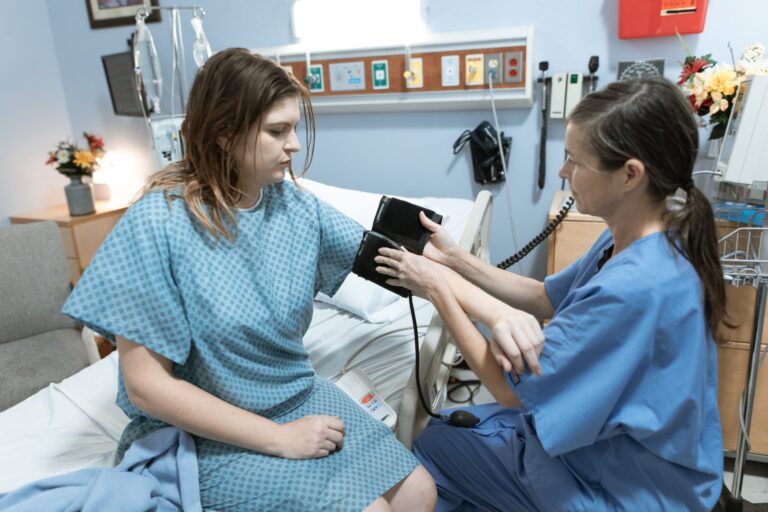
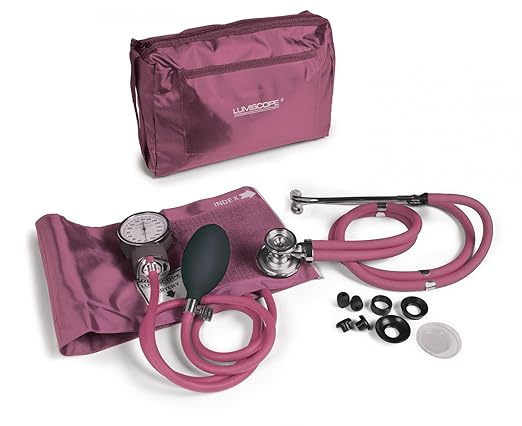
Professional blood pressure monitors
The Professional Blood Pressure Monitor, commonly known as a Sphygmomanometer, stands as a quintessential tool in the arsenal of healthcare professionals. With precision at its core, this device meticulously measures blood pressure, offering accurate and crucial insights into cardiovascular health. The design of the Sphygmomanometer comprises an inflatable cuff, a pressure bulb, and a mercury or aneroid manometer. Trusted for its reliability, it remains a symbol of accuracy in blood pressure monitoring.
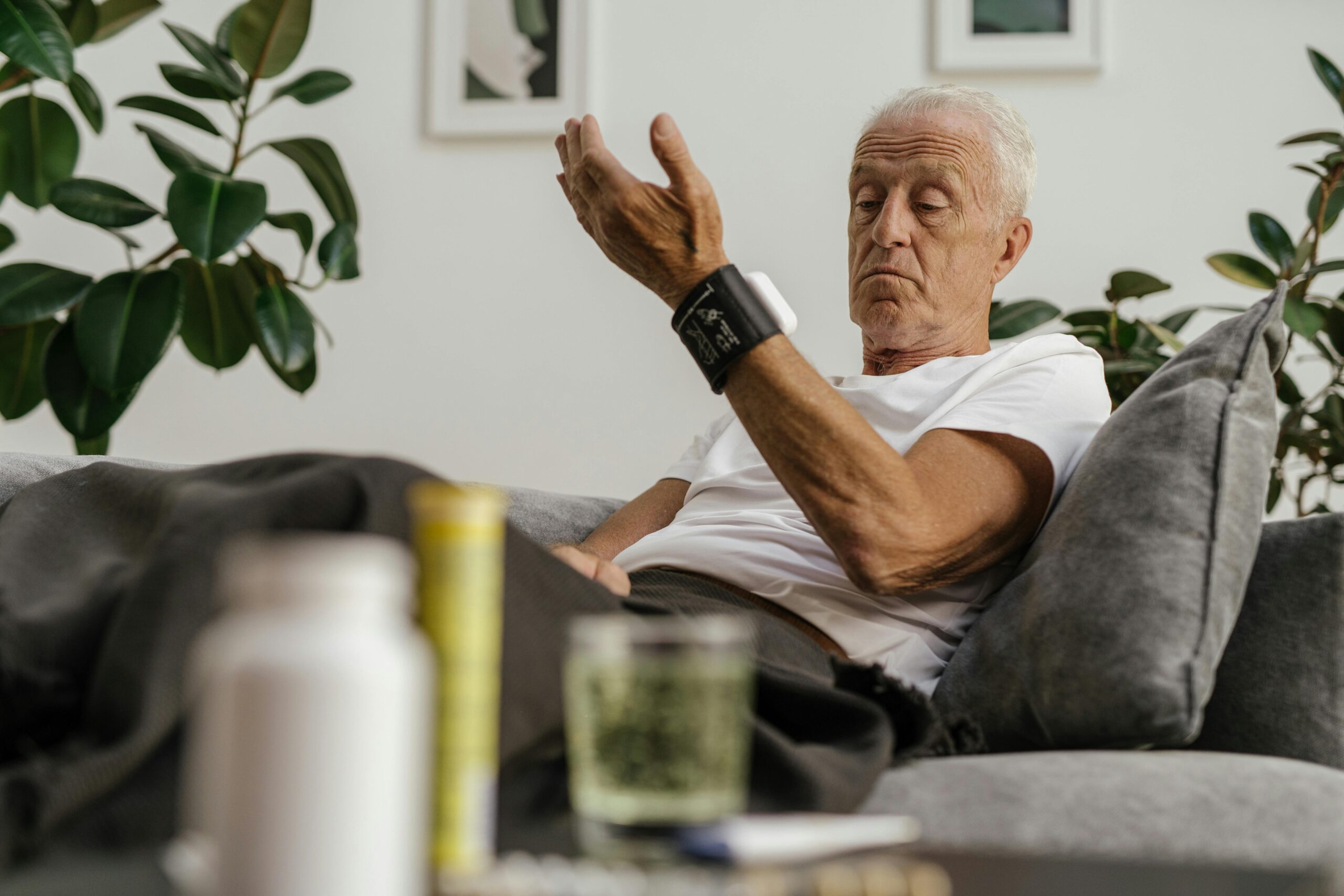
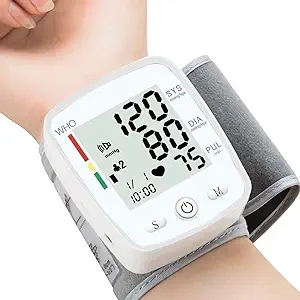
Wrist blood pressure monitors
Models that are easy to carry around and are small and precise for taking your blood pressure rapidly. These monitors are the fastest-growing category in the blood pressure monitor industry because of their ease of use. Compared to upper arm variants, they can be significantly faster because there’s no need to take off a jacket or sweatshirt. They also have the benefit of being able to fit both thin and overweight wearers with the same cuff size because wrist diameter is less impacted by obesity than upper arm diameter.
Features to look for in home blood pressure monitors
Memory:
Your readings from most home blood pressure monitors can be stored for further comparison. The user has the option to store a reading into memory once it has been taken. Many monitors today can hold up to thirty measures, while a select few can actually store 350! Some monitors simply store the previous reading!
Cuff Size:
It’s crucial to use the appropriate size cuff to get an accurate reading. A measurement that is higher is obtained from a cuff that is too small, while one that is too large will result in a reading that is lower than the accurate blood pressure. Measure the diameter of your upper arm at the point where the elbow and shoulder meet while your arm is hanging at your side.
Accuracy:
When evaluating the blood pressure monitor’s accuracy, the pressure variation should not exceed ±3 mmHg or 2%, whichever is higher. These days, most house models come complete with this accuracy thanks to technology.
Power:
While the majority of home blood pressure monitors run on batteries, a number of them have an AC adaptor socket that lets you use an outlet in your house to power them. Not every monitor comes with an adaptor. A typical AC adapter will function, though. Usually included with the monitor is an AA battery, which is the usual size.
Connectivity:
Some blood pressure monitors allow you to print the blood pressure reading. For people who don’t want to spend the time charting each of their unique readings, this option is really helpful. Additionally, there are blood pressure monitors that connect to your computer or phone. The supplementary apps offers trending and analyzing features along with a communication interface.
Taking Your Blood Pressure:
|
|